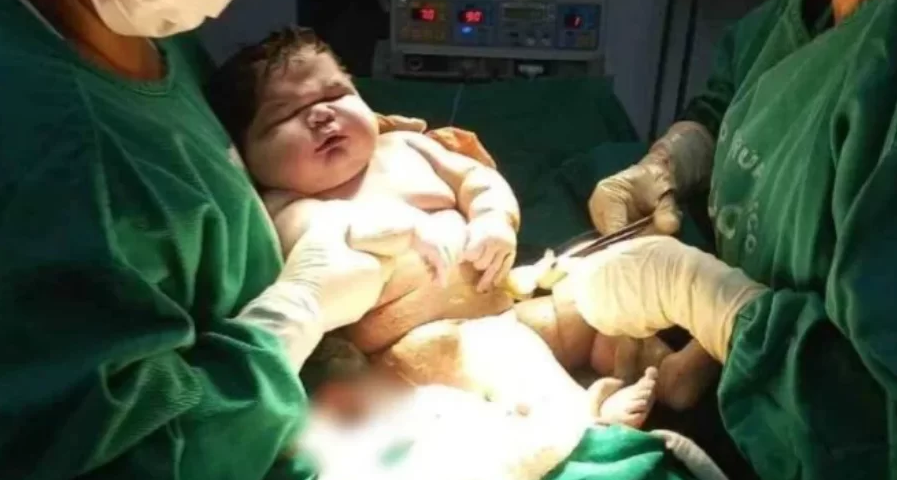
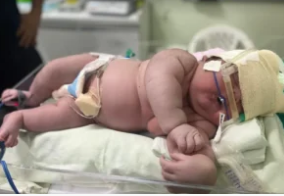
Recently, in Parintins, Amazonas, a woman gave birth to an impressively large baby. Born with 7.3 kilograms and 59 centimeters, Angerson drew attention on social networks for his unusual weight. Despite being born very large, the baby is healthy and does not suffer from any health complications. The explanation for the condition of a giant baby is called macrosomia, and although many people find it cute and curious to see a chubby baby, Dr. Carolina Cunha, an obstetrician-gynecologist, points out that being overweight is not a good indicator and presents health risks.
“We must understand that a big boy is not cute and cute because he is fat. He is a sick boy.” To get an idea of how different a baby is, the average baby weighs around 3kg right after birth, so Angersson is 4kg taller than average. But what dangers could a giant baby face?
Giant Baby: What is embryonic gigantism?
Doctor Carolina Cunha, explains that fetal gigantism is a specific problem when the baby weighs more than 4 kilograms. The main causes are diabetic and obese mothers. However, there are other factors that can lead to this condition, for example: multiple pregnancies, very tall fathers, prolonged pregnancies and male children tend to be larger.
In a previous interview with Vitat, d. Nelson Douglas Eigenbaum, MD, pediatrician, neonatologist, and member of the American Academy of Pediatrics, points to the relationship between diabetes, obesity, and the development of macrosomia.
“A mother with gestational diabetes causes the baby’s blood glucose to rise, yet she has to secrete more insulin, which he mistakes for growth hormone,” explains Dr. Nelson.
What are the consequences of the condition for mother and baby?
First, fetal gigantism can make the route of delivery mandatory by cesarean section. In this way, more safety is guaranteed for both mother and child on the road. Therefore, in case of a normal delivery, the baby may not be able to pass through the vaginal canal.
Generally, when the condition is related to gestational diabetes that is not well controlled, the baby can suffer a series of complications after birth. So the main thing is the risk of developing hypoglycemia, notes dr. carolina This metabolic disorder can cause complications such as brain damage. Therefore, when a child develops hypoglycemia, he may become listless, with tremors and even seizures.
Thus, another consequence of fetal gigantism is the possibility of fractures at birth, such as those of the clavicle, if the route of delivery was normal. Thus, the same can happen with respect to stretching the brachial plexus, which is the set of nerves located between the neck and the shoulder.
Caring for a Giant Baby
doctor. Carolina points out that even during pregnancy it is possible to identify the fetus by the size of the abdomen and by ultrasound scans that estimate the weight of the child by the length of the child. So it is the ultrasound that confirms the condition. Early diagnosis is necessary for monitoring and health care, such as control of diabetes and obesity in the mother.
Finally, the neonatologist also warns that a large baby can develop hypoglycemia in newborns. So in summary, that’s when it ends with a sudden drop in glucose levels between 24 and 72 hours after birth.
The Dr explains. nelson Thus, giant babies are subject to a more careful evaluation by the medical team through check-ups and hypoglycemia control.